- Ultrasound
- PSWD (Pulsed Short-Wave Diathermy)
- Interferential Stimulation
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
- NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation)
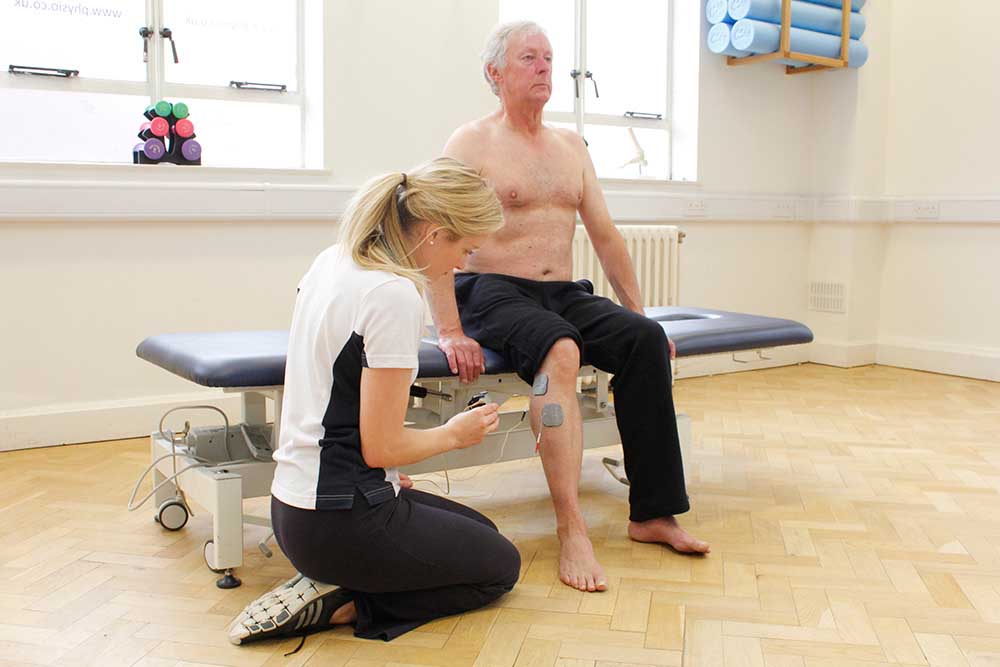 Above: Neurological physiotherapist applying functional electrical stimulaltion treatment to aid mobility
Above: Neurological physiotherapist applying functional electrical stimulaltion treatment to aid mobility Ultrasound
Ultrasound can be used on both chronic and acute conditions and is commonly used in the rehabilitation of muscle, tendon and ligament injuries, haematomas and oedema. High frequency sound waves are focussed around the site of an injury by gently moving an ultrasonic head over the affected area. These sound waves perform a 'micro-massage' deep inside the injured tissues speeding up the healing process.
PSWD (Pulsed Short-Wave Diathermy)
This non-invasive technique uses electromagnetic energy to promote healing within the affected area. Physiotherapists use PSWD to treat a variety of conditions including osteoarthritis, muscle, tendon and ligament injuries, haematomas and oedema.
Interferential Stimulation
Interferential stimulation uses gentle medium frequency electrical currents passed through the affected tissues using conducting pads. This technique can relieve pain, reduce swelling and bruising, and promotes healing by increasing circulation to the injured area.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
TENS is a form of non-invasive pain relief often used in the treatment of chronic pain. The safe and effective technique involves the use of a battery operated device and is delivered across the skin via conducting pads. Two natural processes within the body are stimulated. The tingling sensation of the TENS inhibits the amount of pain signals received by the brain. TENS also increases the levels of the body's own natural pain killing substances called endorphins and enkephalins.
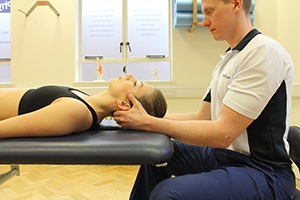
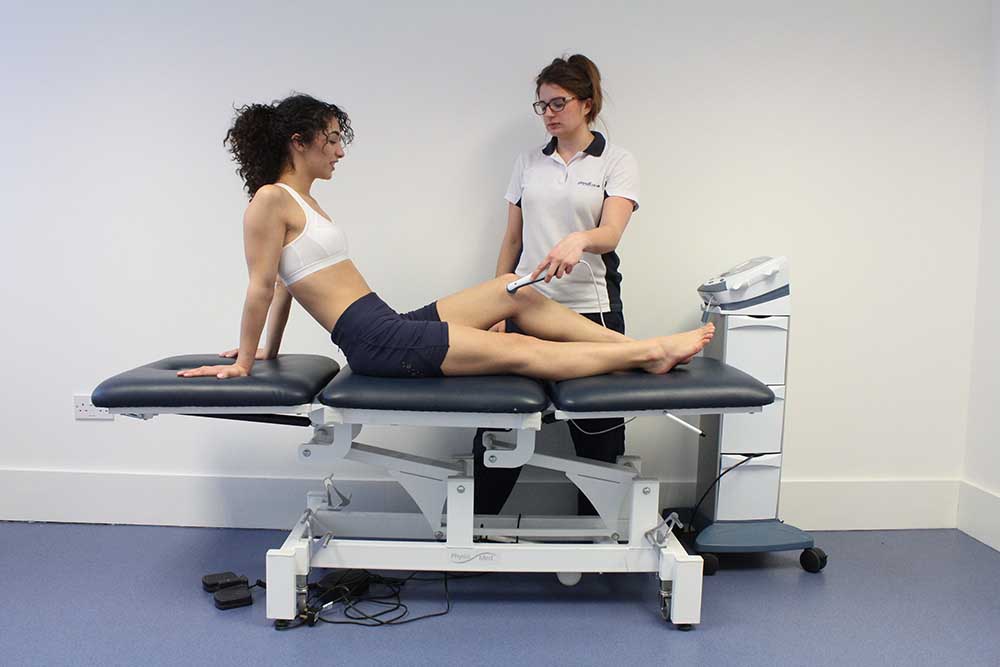 Above: Soft tissue massage of the upper back and trapezius muscles by an experienced physiotherapist
Above: Soft tissue massage of the upper back and trapezius muscles by an experienced physiotherapistNMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation)
NMES is mainly used by Physiotherapists to strengthen very weak muscle groups and in some cases, such as a nerve palsy, maintain muscle strength and speed up recovery of the affected nerve. Its other benefits are; reduction of swelling, relief of pain and wound repair. NMES is similar to TENS in the way that it is electrical energy applied via conducting pads. Excitation is caused in the nerves supplying the muscle group or area to be treated and an excitation, or contraction, is, therefore, caused in this muscle tissue.
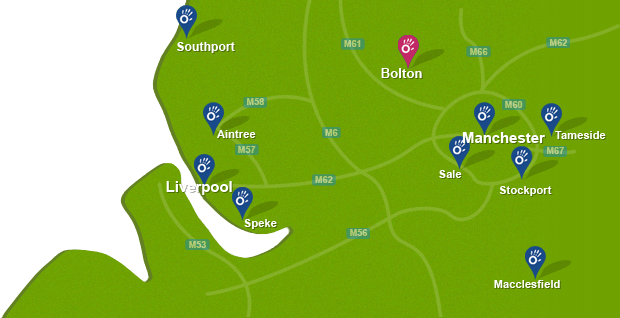
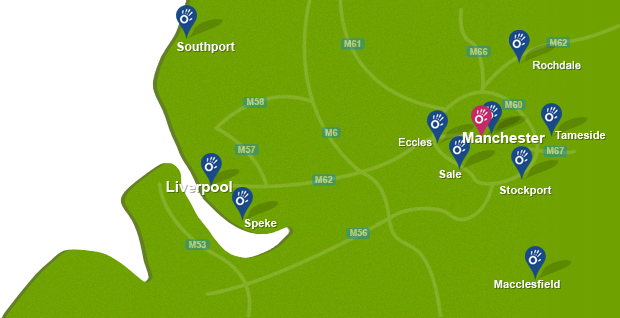
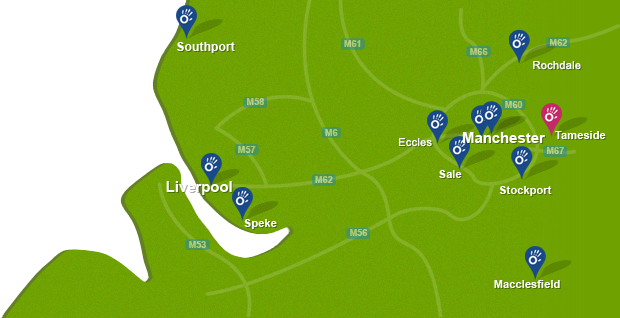
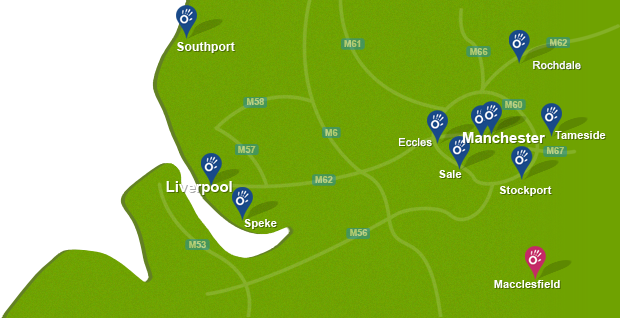
To arrange an appointment book online, call now on 0161 883 0077 or email: office@manchesterphysio.co.uk



 0800 033 7800
0800 033 7800



































 f
f