Muscle tightness is a form of hypertonicity. Hypertonicity is an increase in muscle tone. High muscle tone is the main cause of muscles tightening up.
When muscles are tight, muscle fibres become stiff and rigid which limits movement. Due to excessive tone, the muscle remains in a shortened state causing imbalance in the body. Tight muscles can pull posture out of alignment and can constrict blood flow. The problem of muscles tightening up can be reduced with massage. Massage stimulates blood flow in the muscles, increasing the temperature. An increase in temperature and blood flow allows the muscles to relax.
Once muscles are relaxed and lengthened, posture and movement will improve. Massage therapists at Manchester Physio provide massage therapy services for tight muscles to treat a range of conditions.
Why do muscles go tight?
Muscles become tight for many reasons. Muscles can tighten due to soft tissue damage, increased tone and muscle contractures.
Muscles can become tight due to soft tissue damage. When damage occurs to soft tissues, the body produces collagen fibers as part of the healing process. Collagen fibers are formed around bone, muscle, ligaments and tendons. Collagen fibers can provide different functions due to the arrangement of fibers. Collagen fibers are laid across damaged tissues to help them repair. Collagen fibers are laid in a crisscrossing pattern which can cause knots in muscles. Knots can restrict movement and shorten the muscle. Lack of movement in muscles causes an increase in tightness and produce pain.
Muscles can also become tight due to an increase in tone. Increased tone is tension in the muscle when at rest. Increased tone comes from an increase in excitatory messages from the nervous system. Excitatory messages are stimulated by emotions such as, adrenaline, stress or anxiety. Excitatory message are released from the brain and travel down the spinal cord and into the nerves. The stimulation of nerves causes muscle tension and muscle tone to increase.

Muscles can tighten due to muscle contractures. Muscle contractures are a mechanical response in the muscles which causes muscles to shorten. An increase of muscle tone causes muscle to become hyperactive resulting in constant contraction. Collagen fibers in the muscle are not broken down which restrict movement. Knots are built up in the muscles resulting in the muscle to shorten.
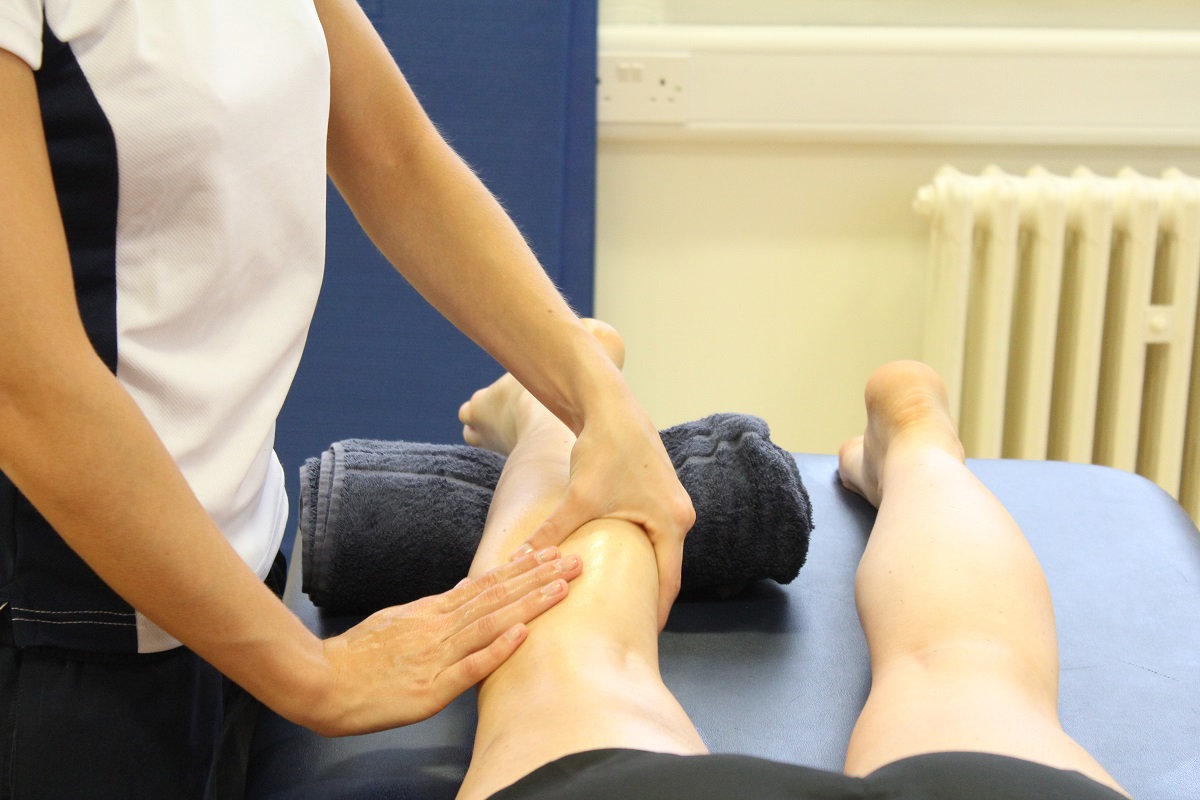
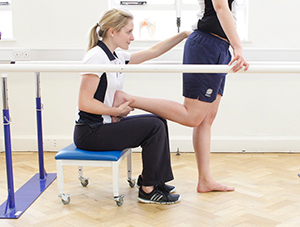
 Above: Trigger point massage of gastrocnemius to release knotted muscle and tightness
Above: Trigger point massage of gastrocnemius to release knotted muscle and tightnessWhat causes tight muscles?
Most common reasons are poor posture and emotional stress. Standing, sitting or lying with poor posture produces tension or load on the muscles. When a muscle is loaded, it naturally resists the load by contracting to overcome the demand. Overtime, the effects of tension (load) can have an effect on the muscles. The contraction or overactive response to load become learned behavior for the muscles and will stay contracted when load is removed. Muscles provide us with everyday movements and therefore can affect joints. Tight muscles affect joint mobility that restricts movement. When joints are immobilised for a length of time, muscles, connective tissue, ligaments and tendons can lose extensibility. Lack of flexibility around a joint leads to tissues being stuck together and encouraging an abnormal cross linking of connective tissues.
There are many reasons why muscles go tight. The causes of tight muscles include:
- Bad posture
- Muscle imbalance
- Over use
- Stress
- Inflexibility
Tight muscles can be the result of muscle imbalance. Muscle imbalance can cause postural changes, restricted movement and pain. Muscle balance is the relationship between tone, strength and length of muscles around a joint. If there is a lack of balance within the muscles it can cause dysfunction in the relationship of how muscles work together and cause imbalance.
Overuse of certain muscles can contribute to tight muscles. Repetitive movements in occupation or exercise can cause small tears or injuries to muscle tissue. The repeated activity does not give sufficient time for healing. Muscles respond to injury by tightening up as a protection from further injury.
The effects of stress can create physical responses in the body leading to tight muscles. Different types of stress can affect how muscles respond. After intense exercise muscles become tight as there has been a physical demand. Blood flow is reduced in tight muscles causing soreness. Emotional stress also can activate an unconscious reflex in the body. Stress causes muscles to contract leading to tight muscles.
Inflexibility in the muscles can restrict movement around joints causing surrounding muscles to tighten. Inflexible muscles are prone to tightness as they do not reach end of range. Inflexibility can lead to serious injuries such as muscles strains and tears.
What types of massage are mainly used for tight muscles?
At Manchester Physio our massage therapists use a variety of massage techniques for tight muscles. Massage is used to treat tight muscles by decreasing tone and breaking down collagen fibres. Common techniques used to decrease tone and break down collagen include: Massage therapists at Manchester Physio use specific massage techniques to decrease tone. Massage techniques used to decrease tone include: Massage is used to treat tight muscles. A range of massage techniques can be used to relieve tight muscles by decreasing tone. Massage techniques such as effleurage, petrissage, kneading and rolling are all used to decrease tone in the muscles. Effleurage is a light stroking technique used to increase temperature of soft tissues and increase blood circulation. An increase of temperature allows the muscles to relax, relieving tension and decreasing tone. Petrissage, kneading and rolling are massage techniques which are used to pick up, squeeze and roll soft tissues. Petrissage, kneading and rolling is used to decrease tone by relieving muscular spasm, increasing fresh oxygen and nutrients and removing toxins.
Massage therapists at Manchester Physio use specific massage techniques to break down collagen fibres. Massage techniques used to break down collagen include: A variety of massage techniques can be used to break down collagen fibres. Collagen fibres are found all over the body. Collagen fibres provide different functions based on the arrangements of the fibers. Collagen fibers can provide strength and support within the soft tissues. The different arrangements of fibres can cause tightness and restrict movement. Kneading, myofascial release, trigger pointing and rolling are effective massage techniques used to break down collagen fibres. Kneading, myofascial release, trigger pointing and rolling relieve congestion around certain areas of muscle. Knots can be formed due to the pattern of collagen fibers laying down. Massage techniques are used to apply pressure and break down collagen fibers.
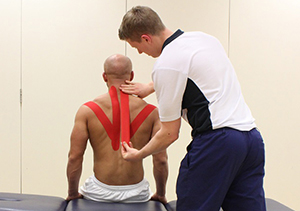
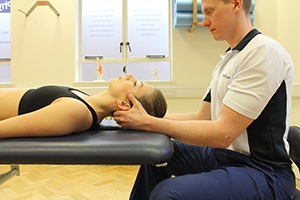
 Above: Massage and stretch of glenohumeral joint to ease tight muscles
Above: Massage and stretch of glenohumeral joint to ease tight musclesWhat are the benefits of massage for tight muscles?
Massage for tight muscles has many benefits. The benefits of massage for tight muscles include: Massage has many benefits to reduce tight muscles. The benefits of massage for tight muscles are reduced tension, decrease pain and improve range of movement.
Massage helps to reduce tight muscles by reducing tension. High muscle tone causes an increase in tension. Massage helps to reduce high muscle tone by increasing blood circulation, increasing temperature of the soft tissues and removing waste products. Massage increases blood circulation into the muscles. An increase of blood circulation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to soft tissues. Massage increases temperature and allows the muscles to relax. Relaxed muscles decrease in tone and reduce tension. Massage also helps reduce tension by removing waste products out of the body. Tension is reduced as waste products are flushed out of the muscle.
Massage helps reduce tight muscles by decreasing pain. Massage helps to decrease pain by interrupting the pain cycle. When pain is felt in the muscles surrounding the area tighten to protect it. An increase of blood circulation allows the muscles to relax. Once the muscles are relaxed pain is decreased and tone is reduced.
Massage reduces tight muscles and improves range of movement. Massage helps improve range of movement by increasing temperature and increasing elasticity. Massage increases temperature of tight muscle by stimulating friction to the area. Friction increases capilliarisation and vasodilation in the blood. Capilliarisation and vasodilation are the increase of number and size of blood cells. Muscle fibres are relaxed as temperature and blood flow increases. The benefit of reduced tightness produces an increase of range of movement.
How does massage for tight muscles help?
Massage helps reduce tight muscles by increasing temperature of soft tissues, increasing blood circulation, breaking down adhesions and decreasing tone. Massage helps treat muscle hypertonicity in the muscles. Hypertonicity in the muscles reduces blood flow and results in muscle tightness. Muscles tighten after exercise, after repetitive motion or long periods of inactivity. Muscle tightness can be treated with a range of massage techniques.
Massage helps reduce tight muscles by increasing temperature of soft tissues. Massage stimulates an increase of temperature by friction against the skin. Friction causes an increase of blood flow to the muscle and temperature to increase. When temperature increases the muscle fibres relax and loosen allowing more movement.
Massage helps relieve tightness in the muscles by increasing blood circulation to the muscles. Restoring circulation to the muscles increases new blood cells to the area stimulating the healing process. Massage relaxes the muscles, separating and loosening muscles fibres. The muscles are elongated and stretched which releases tension and allows more movement.
Massage reduces tightness by applying pressure to knots and breaking adhesions. Pressure points can be used to force out knots in the muscle. Knots and adhesions are formed from a build-up of waste products or high tension in the muscle. Massage breaks down the knots and adhesions and help realign the fibres back to normal form. Relieving knots and adhesions decreases tightness.
Massage helps to decrease tone in the muscles. Massage increases temperature in the soft tissues and stimulates a relaxation response. A relaxation response in the body produces inhibitory messages from the nervous system. Inhibitory messages produce an opposite effect from excitatory messages. Inhibitory messages send relaxing messages to the muscles that decreases tone.
Summary
Muscles tightness can limit flexibility, increase pain and cause further injury. Massage is an effective treatment to release muscle tightness. Massage uses a range of techniques to increase the blood flow, break down inflexible scar tissue and stretch and loosen muscles. Pain is decreased from allowing the muscle to move and restoring blood flow. Massage therapists at Manchester Physio provide massage therapy services for tight muscles to treat a range of conditions.
How can I arrange a massage for tight muscles?
To arrange a massage for tight muscles at Manchester Physio, email us at office@manchesterphysio.co.uk or call 0161 883 0077.



 0800 033 7800
0800 033 7800




































 f
f